Have you ever found yourself jolting awake, gasping for air, or feeling utterly exhausted despite spending enough time in bed? These could be more than just signs of a restless night; they might indicate sleep apnea, a serious sleep disorder that affects millions yet often remains undiagnosed. Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea is crucial, as timely diagnosis and treatment can dramatically improve your quality of life and health. Let’s delve into the signs and symptoms that could signal the need for a professional evaluation.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing throughout the night. These interruptions, known as apneas, can significantly disrupt your sleep cycle and lead to various health complications.
Types of Sleep Apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, causing a blockage of the airway. It’s the most common type, often associated with snoring and physical blockages in the nasal or throat area.
- Central Sleep Apnea: Unlike OSA, central sleep apnea isn’t about physical blockages but rather a failure of the brain to properly control breathing during sleep.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, this condition represents a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea, posing unique challenges for treatment.
Impact on Health:
Sleep apnea affects various aspects of health, from physical to mental well-being. Understanding its types and symptoms is the first step toward getting effective treatment and preventing long-term health issues.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
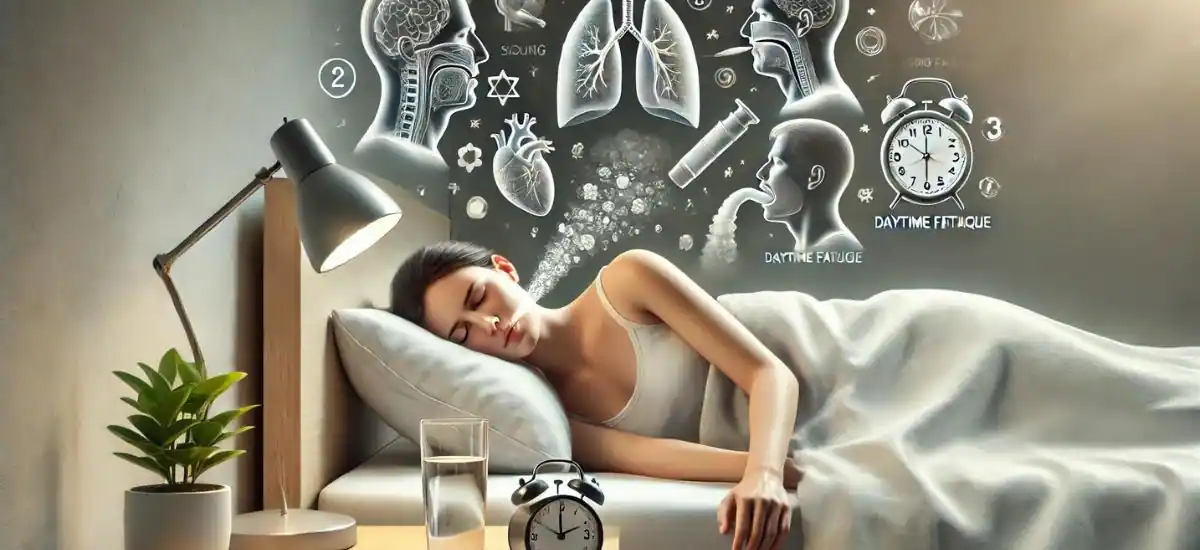

Nighttime Symptoms:
- Loud Snoring: While snoring can be common for many people, excessively loud snoring often punctuated with periods of silence is a hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Breathing Pauses: These are typically noticed by a partner rather than the individual suffering from sleep apnea. Pauses in breathing are followed by gasping or choking as breathing restarts.
- Gasping or Choking at Night: Many patients wake up abruptly gasping for air, a reflexive response to the body’s struggle to resume breathing.
Daytime Symptoms:
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Often, people with sleep apnea experience significant fatigue and drowsiness during the day, regardless of how long they sleep at night. This is due to the poor quality of sleep and constant awakenings.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Frequent interruptions in sleep can lead to problems with focus, memory, and maintaining attention during daytime activities.
- Mood Changes: Irritability, mood swings, and even depression can be symptoms related to the chronic sleep disruption caused by sleep apnea.
Daytime Symptoms Indicative of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea doesn’t just disturb your night; it can significantly impact your day. Here’s what to watch for:
- Unexplained Fatigue: Despite logging enough hours of sleep, you might find yourself feeling inexplicably tired or drowsy throughout the day, which can signal disrupted sleep cycles due to sleep apnea.
- Poor Concentration and Memory: Sleep apnea can leave you feeling foggy and unfocused, affecting your cognitive functions and memory, making daily tasks more challenging.
- Headaches: Waking up with a morning headache is common among those with sleep apnea, likely due to decreased oxygen levels and poor sleep quality during the night.
- Irritability and Mood Changes: Chronic sleep disruption can lead to significant mood swings, irritability, or even depression, affecting your overall emotional well-being.
Physical Symptoms That May Indicate Sleep Apnea
Recognizing the physical symptoms of sleep apnea can lead you to seek necessary medical advice:
- Dry Mouth or Sore Throat Upon Waking: Many people with sleep apnea may wake up with a dry mouth or sore throat, a result of breathing through the mouth during sleep interruptions.
- Frequent Nighttime Urination: Known as nocturia, this symptom can be exacerbated by sleep apnea due to the body’s physiological responses to disrupted breathing.
- Decreased Libido: The exhaustion and stress caused by chronic sleep disruption can also affect sexual desire and performance.
Risk Factors and Complications
Understanding who is at risk and the potential complications can highlight the importance of managing sleep apnea:
- Risk Factors:
- Obesity: A major risk factor due to the potential for fatty tissue in the throat area, which can obstruct breathing.
- Age and Gender: Older adults and males are more commonly affected, though sleep apnea can occur at any age and in both sexes.
- Family History and Genetics: Genetics can play a role in the structure of the airways and the risk of sleep apnea.
- Use of Alcohol or Sedatives: These substances relax the muscles in the throat, which can exacerbate the symptoms of sleep apnea.
- Complications If Untreated:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Sleep apnea can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke, and irregular heartbeats.
- Daytime Fatigue: Severe daytime drowsiness can lead to reduced productivity and increased risk of accidents.
- Mental Health Issues: Ongoing disruption of sleep can lead to serious mental health issues, including depression and anxiety.
When to See a Doctor
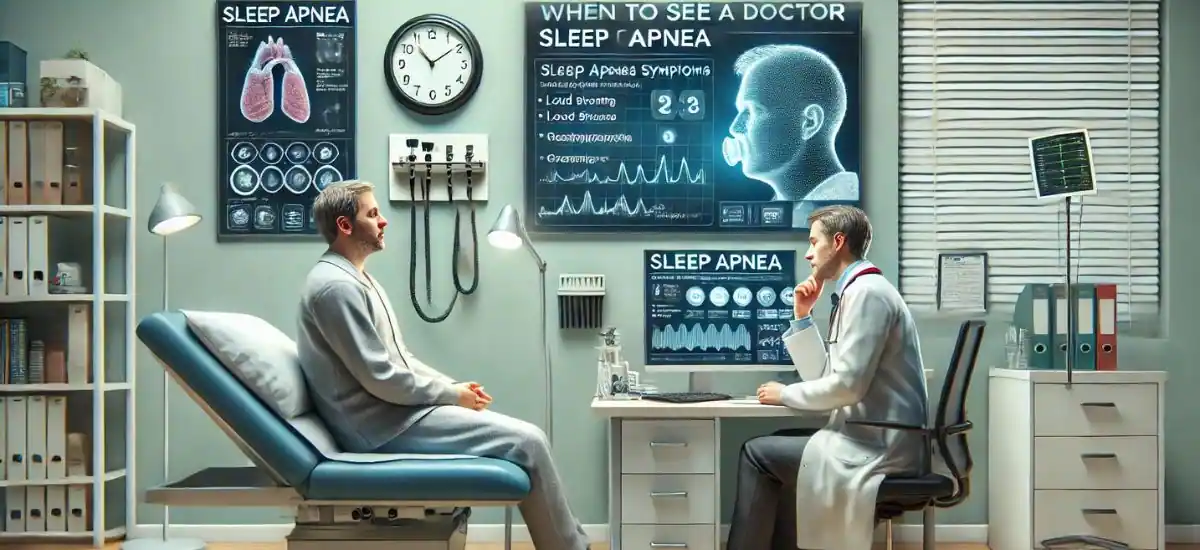

Recognizing when to seek professional help can make a significant difference in managing sleep apnea effectively:
- Persistent Symptoms: If you or your partner notice chronic snoring accompanied by breathing pauses, or if you experience excessive daytime sleepiness regularly, it’s time to consult a doctor.
- Impact on Daily Life: When symptoms start affecting your daily activities, mood, and overall quality of life, professional evaluation becomes essential.
- Observation by Others: Often, the first signs of sleep apnea are noticed by others observing your sleep patterns. If someone comments on your unusual sleep behaviors, such as choking or gasping for air, consider seeing a specialist.
Diagnostic Approaches and Treatments
Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea:
- Sleep Study (Polysomnography): This test is conducted overnight and monitors several body functions during sleep, including brain electrical activity, eye movement, muscle activity, heart rate, respiratory effort, air flow, and blood oxygen levels.
- Home Sleep Apnea Testing: For less complex cases, a home sleep test might be suggested, which is a simplified version of the polysomnography and can be done in your own bed.
Common Treatments for Sleep Apnea:
- CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): The most common treatment involving a machine that uses a hose and mask or nosepiece to deliver constant and steady air pressure to keep your airways open during sleep.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, quitting smoking, and avoiding alcohol and sleeping pills are often recommended to reduce symptoms.
- Oral Appliances: Designed to keep the throat open, these are sometimes used as an alternative to CPAP for mild to moderate sleep apnea.
- Surgery: In cases where other treatments fail, various surgical options like tissue removal, jaw repositioning, or implants may be considered to increase the size of the airway.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of sleep apnea and the importance of early diagnosis is crucial for effectively managing this sleep disorder. By recognizing the signs early and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and prevent the onset of more severe complications associated with sleep apnea. Remember, a proactive approach and timely treatment can make all the difference in ensuring healthy, restorative sleep.