Ever noticed a red, swollen spot on your skin that feels tender to touch? You might be looking at a bacterial skin infection, a common issue that can range from mild to severe. These infections strike when bacteria enter through cuts or breaks in the skin. Recognizing the signs early is your best shot at a quick recovery, so let’s dive into the essentials of bacterial skin infections—what they are, why they occur, and how to spot them before they spread.
Types of Bacterial Skin Infections
- Impetigo: Commonly affects children and appears as red sores or blisters that can ooze and form a crust—truly uncomfortable!
- Cellulitis: This deep infection, marked by red, swollen skin that feels hot and tender, can occur anywhere on the body and needs quick medical attention.
- Folliculitis: Watch out for small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles, the telltale signs of folliculitis.
- Boils and Carbuncles: These are your larger, more painful buddies, often starting as red, tender lumps that quickly fill with pus.
Tip: If you’re dealing with something that looks like it’s more than just a pimple or a rash, it’s time to pay attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
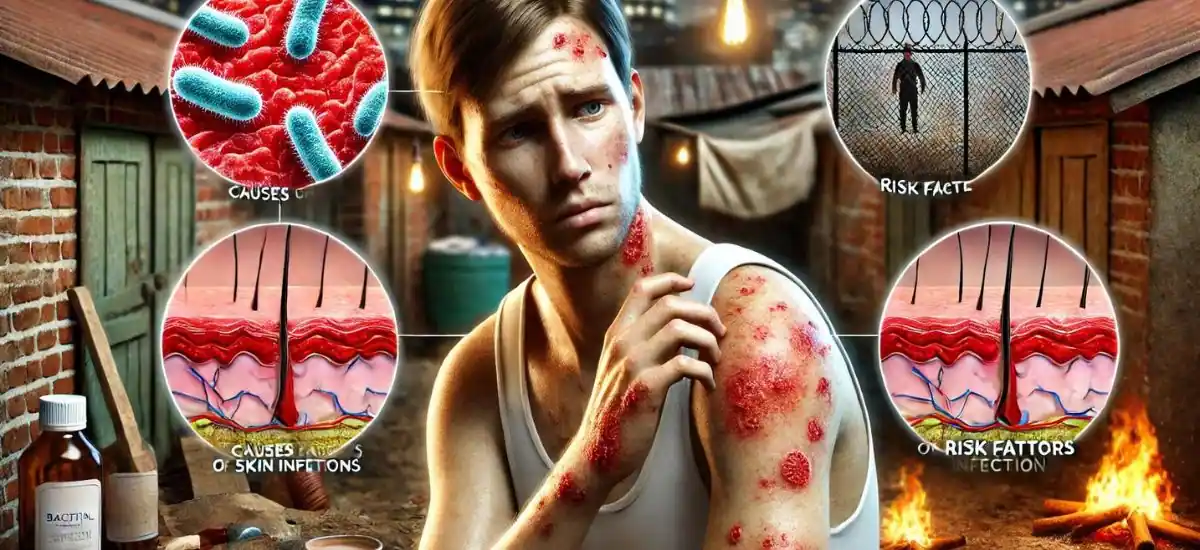

- Bacterial Culprits: Most skin infections are caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria, which can turn a tiny scratch into a big problem.
- Risk Factors: Things like poor hygiene, existing skin conditions such as eczema, or a weakened immune system can increase your chances of developing an infection.
Prevention Pointer: Keeping your skin clean and well-maintained is your first line of defense against these pesky bacterial invaders.
Symptoms of Bacterial Skin Infections
- General Indicators: Look for redness, swelling, pain, or warmth in the affected area—classic red flags that shouldn’t be ignored.
- Specific Symptoms by Type:
- Impetigo: Itchy rash and fluid-filled blisters that develop a honey-colored crust.
- Cellulitis: Red, swollen skin that feels hot and tender, often with fever.
- Folliculitis: Bumps or pimples around hair follicles, sometimes with pus.
- Boils: Red, swollen, and painful lumps under the skin that may burst and drain pus.
When to Worry: If you notice any of these symptoms spreading rapidly, accompanied by fever or a feeling of warmth, it’s time to seek medical advice.
Diagnosis of Bacterial Skin Infections
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will examine the affected skin to identify the type of infection based on appearance and symptoms.
- Laboratory Tests: Skin swabs or cultures may be taken to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection, which helps in selecting the most effective treatment.
Insider Tip: Early diagnosis can prevent most bacterial skin infections from becoming serious, so don’t hesitate to consult a doctor if you’re unsure about a skin issue.
Treatment Options
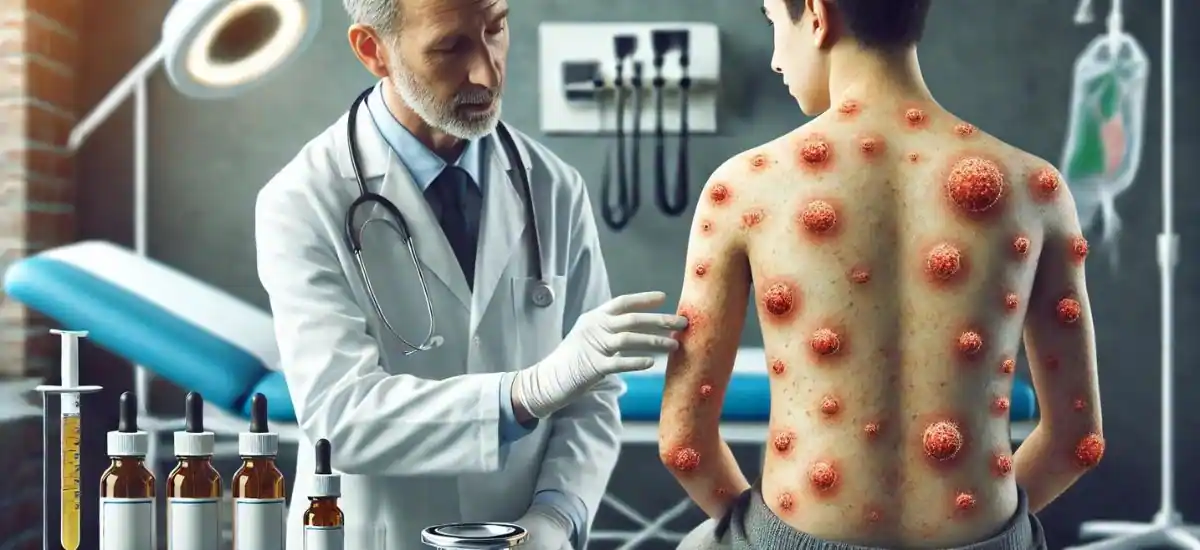
- Topical Antibiotics: For mild infections like impetigo, a topical antibiotic cream or ointment may be prescribed to apply directly to the skin.
- Oral Antibiotics: More serious infections like cellulitis require oral antibiotics to help fight the bacteria from within.
- Advanced Care: In cases of severe or persistent infections, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary, and hospitalization might be recommended to monitor the response to treatment.
Preventive Measures: Alongside treatment, maintaining good personal hygiene and proper wound care are crucial to prevent further infections or recurrence.
Prevention Tips
Keeping Bacterial Skin Infections at Bay:
- Hygiene: Regular hand washing and bathing with soap and water are fundamental in preventing skin infections.
- Care for Cuts and Scrapes: Clean and cover any wounds promptly to prevent bacteria from entering the skin.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Items like towels, razors, or clothing can harbor bacteria and should not be shared.
- Healthy Skin Care Routine: Moisturize your skin to prevent cracks and dryness that can make it easier for bacteria to invade.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine to boost your immune system, making it easier for your body to fight off infections.
Complications of Untreated Bacterial Skin Infections
The Risks of Delaying Treatment:
- Spread of Infection: Bacteria can spread to other parts of the body, leading to more severe infections or entering the bloodstream, a condition known as sepsis.
- Permanent Skin Damage: Recurrent or severe infections can cause scarring or changes in skin color and texture.
- Increased Medical Costs: Delaying treatment often leads to more complex and expensive medical interventions later on.
Awareness is Key: Recognizing symptoms early and seeking treatment can prevent most of these complications.
Conclusion
Bacterial skin infections, though common, should not be taken lightly. Recognizing the signs early and understanding how to prevent and treat infections are crucial steps in managing your health. Armed with this knowledge, you can take proactive measures to protect yourself and your loved ones from potential complications. Remember, maintaining good hygiene and caring for your skin are simple yet effective ways to keep bacterial infections at bay. If you suspect a bacterial skin infection, consult a healthcare professional promptly to receive the appropriate care.


